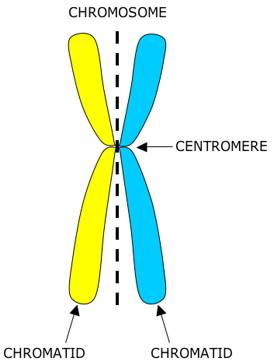
Homozygous: two same alleles of a gene on each chromosome on a homologous pair
Heterozygous: one of each allele of a gene on each chromosome on a homologous pair
Rescessive: an allele only expressed if the dominant allele is absent or if [the recessive gene] is homozygous.
Dominant: an allele that always express itself whether it is heterozygous or homozygous
Homologous pair: a chromosome containing a maternal and paternal chromatid joined together. (these have the same gene but may have different alleles)
Chromatid: each of the two threadlike strands that chromosomes divide into during mitosis.
Saturday, September 17, 2016
3.16 Understand that genes exist in alternative forms called alleles which give rise to differences in inherited characteristics
Genes exist in alternative forms called alleles. These control the differences in inherited characteristics.
Extra information:
Alleles can be dominant or recessive, homozygous or heterozygous. They are written as big or small letters. Eg: Aa or AA or aa. This is known as a genotype. The physical characteristic it codes for is called a phenotype.
Extra information:
Alleles can be dominant or recessive, homozygous or heterozygous. They are written as big or small letters. Eg: Aa or AA or aa. This is known as a genotype. The physical characteristic it codes for is called a phenotype.
3.15 Describe a DNA molecule as two strands coiled to form a double helix, the strands being linked by a series of paired bases: adenine (A) with thymine (T), and cytosine (C) with guanine (G)
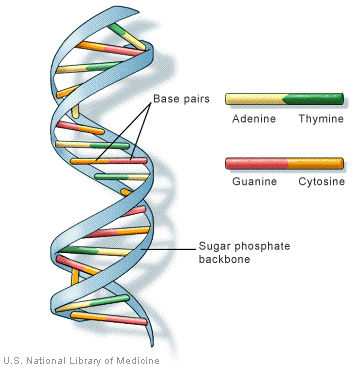
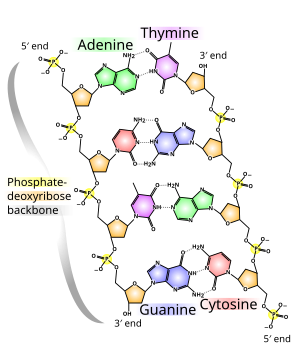
Above, you can see an image of the structure of DNA. It is made up of two coiled strands, known as a sugar phosphate backbone. As the name suggests, it is made up of a sugar and a phosphate (alternating). The base pairs are the 'coding'. It is believed that every living thing has the same base pairs:
- Adenine (A)
- Thymine (T)
- Guanine (G)
- Cytosine (C)
Adenine always pairs up with thymine, guanine always pairs up with cytosine. The order in which these are paired in is what makes up the 'coding' of an organism.
(Virtual flashcards on this topic can be found here, or click 'inheritance flashcards' on the right hand side menu)
Friday, September 16, 2016
3.14 Understand that a gene is a section of a molecule of DNA and that a gene codes for a specific protein
3.13 Understand that the nucleus of a cell contains chromosomes on which genes are located
If you unwrapped a chromosome, you would see it is essentially just strands of DNA coiled around a protein. DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid (you don't need to know that).
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)