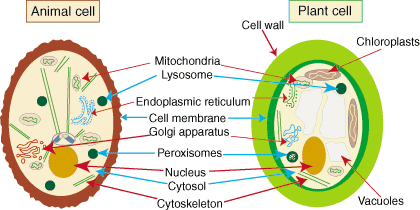
Cell structures
- Nucleus - controls the cell's behavior
- Cytoplasm - makes up most of the cell, a gelatine-like subtance
- Cell membrane - a thin wall that keeps the cell together
- Cell wall - a harder, outer wall that keeps the cell's shape and stops it from bursting when it is full of water
- Chloroplast - allows the organism to photosynthesize: to produce glucose from water and carbon dioxide
- Vacuole - Where cell sap is stored, along with other nutrients
Key
Yellowish orange = Features in both plant and animal cells
Green = Typically associated with plant cells
Pale purple = Typically associated with plant cells, but a small temporary vacuole can be found in animal cells too
 |
| Figure 1: An unnecessarily complicated comparison |
No comments:
Post a Comment